Routing EIGRP
Przygotowanie, scenariusz
Info
Do realizacji tego zadania wymagany będzie dowolnie wybrany emulator np. Cisco Modeling Labs, GNS3, EVE-NG oraz dostęp do obrazów Cisco IOS.
Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) to dynamiczny protokół routingu stworzony przez Cisco. Protokół ten często nazywany hybrydowym ponieważ łączy cechy Distance Vector i Link-State.
Topologia
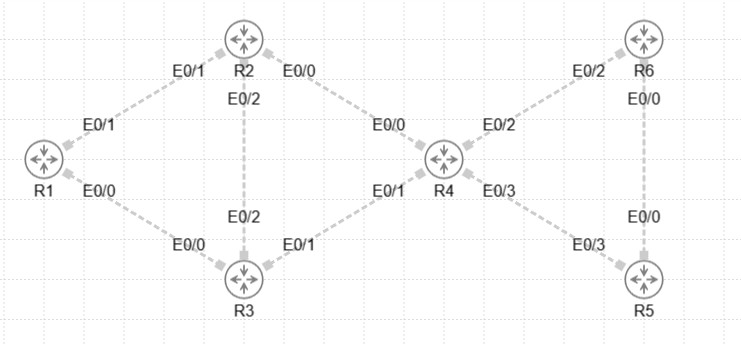
Adresacja
- R1 e0/0 - 172.16.12.1/24
- R1 e0/1 - 172.16.13.1/24
- R1 lop0 - 10.0.0.1/32
- R2 e0/0 - 172.16.12.2/24
- R2 e0/1 - 172.16.24.2/24
- R2 e0/2 - 172.16.23.2/24
- R2 lop0 - 10.0.0.2/32
- R3 e0/0 - 172.16.34.3/24
- R3 e0/1 - 172.16.13.3/24
- R3 e0/2 - 172.16.23.3/24
- R3 lop0 - 10.0.0.3/32
- R4 e0/0 - 172.16.34.4/24
- R4 e0/1 - 172.16.24.4/24
- R4 e0/2 - 172.16.46.4/24
- R4 e0/3 - 172.16.45.4/24
- R4 lop0 - 10.0.0.4/32
- R5 e0/0 - 172.16.56.5/24
- R5 e0/3 - 172.16.45.5/24
- R5 lop0 - 10.1.0.5/32
- R6 e0/0 -
- R6 e0/2 -
- R6 lop0 - 10.1.0.6/32
Konfiguracja R1
Tryb konfiguracyjny i zmiana nazwy urządzenia.
inserthostname-here#configure terminal
inserthostname-here(config)#hostname R1
Adresacja interfejsów.
R1(config)#interface ethernet0/0
R1(config-if)#ip address 172.16.12.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#no shutdown
R1(config)#interface ethernet0/1
R1(config-if)#ip address 172.16.13.1 255.255.255.0
R1(config-if)#no shutdown
R1(config)#interface loopback0
R1(config-if)#ip address 10.0.0.1 255.255.255.255
R1(config-if)#no shutdown
Konfiguracja R2
Tryb konfiguracyjny i zmiana nazwy urządzenia.
inserthostname-here#configure terminal
inserthostname-here(config)#hostname R2
Adresacja interfejsów.
R2(config)#interface ethernet0/0
R2(config-if)#ip address 172.16.12.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no shutdown
R2(config)#interface ethernet0/1
R2(config-if)#ip address 172.16.24.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no shutdown
R2(config)#interface ethernet0/2
R2(config-if)#ip address 172.16.23.2 255.255.255.0
R2(config-if)#no shutdown
R2(config)#interface loopback0
R2(config-if)#ip address 10.0.0.2 255.255.255.255
R2(config-if)#no shutdown
Konfiguracja R3
Tryb konfiguracyjny i zmiana nazwy urządzenia.
inserthostname-here#configure terminal
inserthostname-here(config)#hostname R3
Adresacja interfejsów.
R3(config)#interface ethernet0/0
R3(config-if)#ip address 172.16.34.3 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#no shutdown
R3(config)#interface ethernet0/1
R3(config-if)#ip address 172.16.13.3 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#no shutdown
R3(config)#interface ethernet0/2
R3(config-if)#ip address 172.16.23.3 255.255.255.0
R3(config-if)#no shutdown
R3(config)#interface loopback0
R3(config-if)#ip address 10.0.0.3 255.255.255.255
R3(config-if)#no shutdown
Konfiguracja R4
Tryb konfiguracyjny i zmiana nazwy urządzenia.
inserthostname-here#configure terminal
inserthostname-here(config)#hostname R4
Adresacja interfejsów.
R4(config)#interface ethernet0/0
R4(config-if)#ip address 172.16.34.4 255.255.255.0
R4(config-if)#no shutdown
R4(config)#interface ethernet0/1
R4(config-if)#ip address 172.16.24.4 255.255.255.0
R4(config-if)#no shutdown
R4(config)#interface ethernet0/2
R4(config-if)#ip address 172.16.46.4 255.255.255.0
R4(config-if)#no shutdown
R4(config)#interface ethernet0/3
R4(config-if)#ip address 172.16.45.4 255.255.255.0
R4(config-if)#no shutdown
R4(config)#interface loopback0
R4(config-if)#ip address 10.0.0.4 255.255.255.255
R4(config-if)#no shutdown
Konfiguracja R5
Tryb konfiguracyjny i zmiana nazwy urządzenia.
inserthostname-here#configure terminal
inserthostname-here(config)#hostname R5
Adresacja interfejsów.
R5(config)#interface ethernet0/0
R5(config-if)#ip address 172.16.56.5 255.255.255.0
R5(config-if)#no shutdown
R5(config)#interface ethernet0/3
R5(config-if)#ip address 172.16.45.5 255.255.255.0
R5(config-if)#no shutdown
R5(config)#interface loopback0
R5(config-if)#ip address 10.1.0.5 255.255.255.255
R5(config-if)#no shutdown
Konfiguracja R6
Tryb konfiguracyjny i zmiana nazwy urządzenia.
inserthostname-here#configure terminal
inserthostname-here(config)#hostname R6
Adresacja interfejsów.
R6(config)#interface ethernet0/0
R6(config-if)#ip address 172.16.56.6 255.255.255.0
R6(config-if)#no shutdown
R6(config)#interface ethernet0/2
R6(config-if)#ip address 172.16.46.6 255.255.255.0
R6(config-if)#no shutdown
R6(config)#interface loopback0
R6(config-if)#ip address 10.1.0.6 255.255.255.255
R6(config-if)#no shutdown
Konfiguracja EIGRP
Skonfigurujemy protokół EIGRP w trybie named wskazujący adresację dla AS 10 dla wszystkich zaadresowanych interfejsów.
Router R1.
R1(config)#router eigrp ADMIN
R1(config-router)#address-family ipv4 unicast autonomous-system 10
R1(config-router-af)#eigrp router-id 10.0.0.1
R1(config-router-af)#network 0.0.0.0
R1(config-router-af)#no shutdown
Router R2.
R2(config)#router eigrp ADMIN
R2(config-router)#address-family ipv4 unicast autonomous-system 10
R2(config-router-af)#eigrp router-id 10.0.0.2
R2(config-router-af)#network 0.0.0.0
R2(config-router-af)#no shutdown
Na routerze R1 mamy informację o dołączeniu sąsiada do naszego utworzonego AS.

Router R3.
R3(config)#router eigrp ADMIN
R3(config-router)#address-family ipv4 unicast autonomous-system 10
R3(config-router-af)#eigrp router-id 10.0.0.3
R3(config-router-af)#network 0.0.0.0
R3(config-router-af)#no shutdown
Router R4.
R4(config)#router eigrp ADMIN
R4(config-router)#address-family ipv4 unicast autonomous-system 10
R4(config-router-af)#eigrp router-id 10.0.0.4
R4(config-router-af)#network 0.0.0.0
R4(config-router-af)#no shutdown
Router R5.
R5(config)#router eigrp ADMIN
R5(config-router)#address-family ipv4 unicast autonomous-system 10
R5(config-router-af)#eigrp router-id 10.0.0.5
R5(config-router-af)#network 0.0.0.0
R5(config-router-af)#no shutdown
Router R6.
R6(config)#router eigrp ADMIN
R6(config-router)#address-family ipv4 unicast autonomous-system 10
R6(config-router-af)#eigrp router-id 10.0.0.6
R6(config-router-af)#network 0.0.0.0
R6(config-router-af)#no shutdown
Sprawdźmy jak wygląda tablica sąsiedztwa na routerze R4.
R4#show ip eigrp neighbors

Zobaczmy również jak wygląda tablica routingu na routerze R1
R1#show ip route
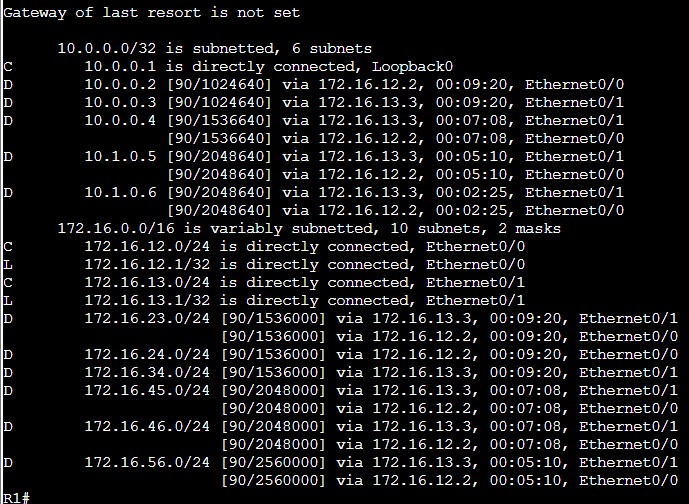
Ponieważ wszystkie połączenia w przypadku mojego emulatora są takie same przez co koszt będzie równomierny to do każdej sieci prowadzą dwie trasy. Czas na więcej szczegółów.
R1#show ip eigrp topology
EIGRP ładuje po dwie trasy do każdej sieci co powoduje uruchomienie Equal-Cost Multi-Path routing (ECMP).

Popsujmy to trochę i ustawmy inną przepustowość dla interfejsu ethernet0/0.
R1(config)#interface ethernet0/0
R1(config-if)#bandwidth 300
Sprawdźmy raz jeszcze tablice routingu oraz topologię EIGRP.
R1#show ip route
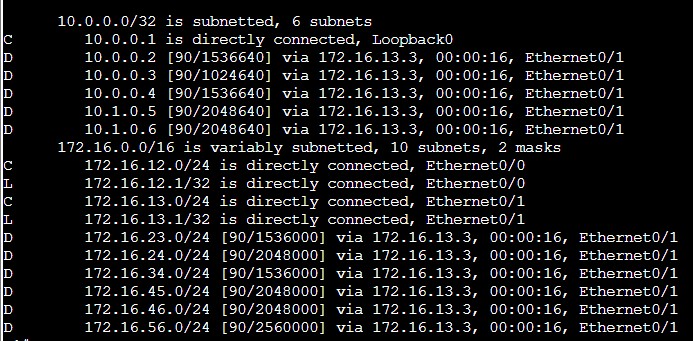
R1#show ip eigrp topology
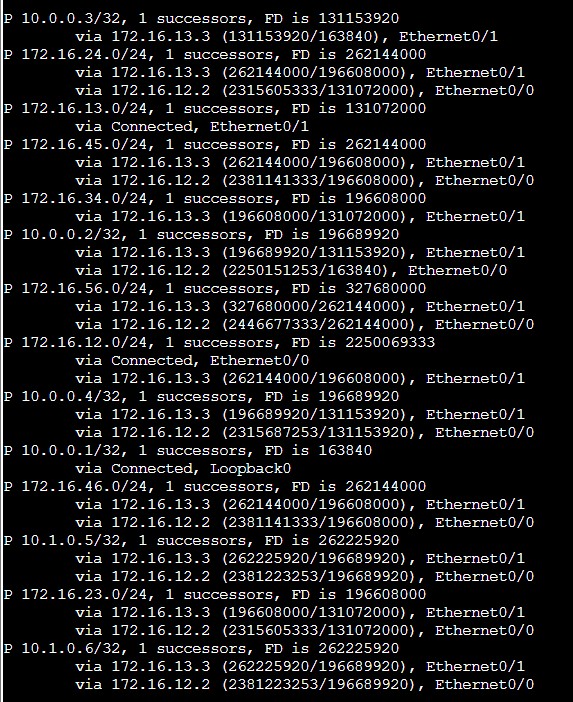
Success
Wszystkie przykłady są tylko formą zainteresowania danym zagadnieniem. Zachęcam do zapoznania się ze szczegółami zawartymi w dokumentacji autora lub producenta
🕞 Ostatnia aktualizacja 23.03.2025
